March 19 (Bloomberg) – Russia’s war in Ukraine, which has caused a humanitarian crisis and convulsed global financial markets, is now threatening to crush an $81 billion economy more than 4,000 miles away in the Indian Ocean.
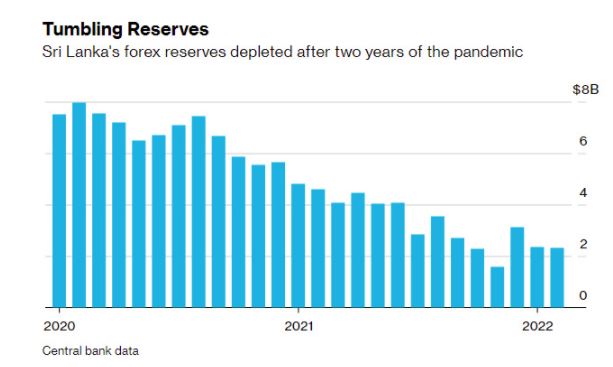
Hit by soaring oil import costs and a dip in tourism revenue, Sri Lanka is racing to avert a default amid dwindling foreign-exchange holdings. With inflation already at 15% — the worst in Asia — the conflict is only making it harder for the tropical island located off the southern tip of India. Fuel shortages and blackouts lasting as long as seven hours have become daily routine, while the wait gets longer at gas stations where prices surged almost 50% this month.
For similar articles, join our Telegram channel for the latest updates. – click here
Authorities are struggling to contain the crisis. They’ve raised interest rates, devalued the local currency and placed curbs on non-essential imports. But with a meager $2 billion in forex reserves and $7 billion in debt payments due this year, the battle is turning uphill. The government this week finally abandoned its reluctance to seek help from the International Monetary Fund and President Gotabaya Rajapaksa pledged to fulfill Sri Lanka’s obligations.
“Seeking help from the IMF is the most feasible way to get out of the crisis,” said Ankur Shukla, a Mumbai-based economist with Bloomberg Economics. “The Russia-Ukraine war has worsened the already weak external balances situation, increasing the gap between external financial requirements and financing sources available.”
READ: IMF to begin talks with Sri Lanka on program to support the country
One of Europe’s worst conflicts since World War II couldn’t have come at a worse time for Sri Lanka, which is still recovering from a brutal 30-year ethnic strife that ended in 2009. The South Asian country has sought to revive growth since, spending millions on tourism infrastructure, until the pandemic dealt a blow to its plans. The crisis also shows how Russia’s war is putting some of the fragile developing economies at risk and imperiling decades of efforts to lift millions out of poverty.
In South Asia, other vulnerable countries include Bangladesh, Maldives, Nepal and Pakistan, Shukla said. Though direct trade and financial linkages with Russia and Ukraine are limited, the “price and supply shocks are powerful,” he wrote in a note on March 9.
With a population of about 22 million, Sri Lanka is a net importer of goods from medicines to fuel. In December, petroleum products accounted for about 20% of inbound shipments and the cost jumped 88% from a year earlier. The increase in oil prices this year is adding to the burden.
READ: Lankan Finance Minister meets Indian Foreign Minister

The country has also been paying off external debt it piled on to help rebuild an economy scarred by the bloody civil war between the majority Buddhist Sinhalese and a Tamil minority that’s predominantly Hindu. That has been draining its forex reserves.
Another pain point is tourism revenue. About 30% of visitors this year were from Russia, Ukraine, Poland and Belarus, and the war is threatening to turn off that tap. Sri Lanka earned $3.6 billion from tourism in 2019 before the pandemic slashed that to less than a fifth two years later, official data show.
The central government’s foreign-owned debt stood at $32 billion as of November. Optimism that the government will soon manage to reach a deal with the IMF has already spurred a rally in the country’s dollar bonds. An offshore bond due 2030 rallied to 49 cents to the dollar from a record low of 38.9 cents on March 9, while one-year default probability has dropped to 18.2% from as much as 31.3% in late December, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
The nation’s international bonds need to be restructured by July as Sri Lanka doesn’t have the necessary resources to pay the $1 billion due that month, Citigroup Inc. said in a February note.
“A scenario we envisage is for an Ecuador-style restructuring where the existing stock of bonds are exchanged into three longer-dated bonds with a reduction in coupon rates,” Nomura Holdings analysts led by Nicholas Yap wrote in a note this week. They said coupon rates may drop to 4%-5% from 5%-8% though a haircut of more than 10% on the principal will be unpalatable to most bondholders. Recovery value could be 50-60 cents on the dollar assuming an exit yield of about 8%-9%, according to Nomura.
Back at home, Central Bank of Sri Lanka Governor Ajith Nivard Cabraal has raised borrowing costs and devalued the rupee, while also urging restrictions on non-essential imports of around 300 items from electronic appliances to apples and increases in fuel prices and power tariffs.
“The government seems to be reacting positively and that would help steer the economy to calmer waters in this time of unprecedented global challenges,” Cabraal said by phone last week.
Subscribe to our Telegram channel for the latest updates from around the world